Blue-eyed Black Lemur (Eulemur flavifrons)
This species of lemur is almost exclusively found on the remote Sahamalaza peninsula. The blue-eyed black lemur was only re-discovered in 1983, after more than a century of uncertainty about its existence.
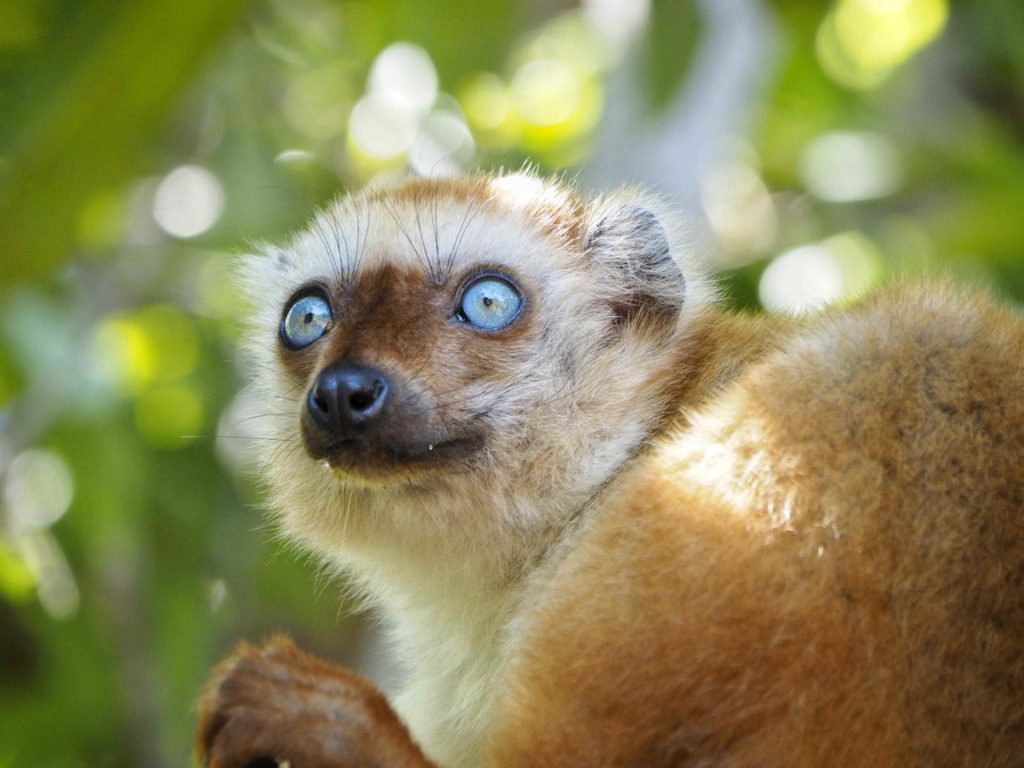

© Sam Cotton – Bristol Zoological Society
They favour primary and secondary sub-humid forests and can also be found on coffee and citrus plantations in northwest Madagascar and in the Ankarafa Forest, which includes primary and secondary forest fragments and is home to the AEECL Field Research Station. This area is believed to accommodate one of the largest connected populations of blue-eyed black lemurs (Schwitzer et al. 2005).
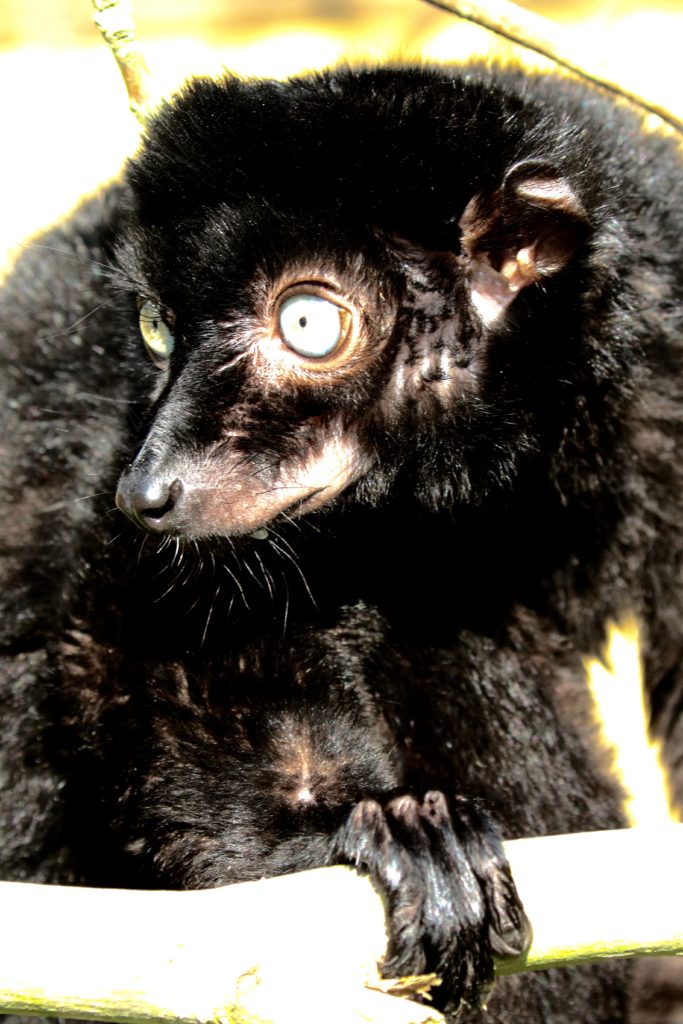
These medium sized lemurs are at threat from the destruction of the forests and illegal hunting and trapping and their exact numbers are unknown. They are classed as Critically Endangered by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red Data List.


